|
|
My Screen Recorder: File Formats
|
File Formats
My Screen Recorder can store its recordings in two file formats: WMV and AVI. By default, recordings are stored as Windows Media Video (WMV) files. This format gives smaller file sizes for any given quality setting than AVI. Generally, we recommend using AVI files only if you plan to edit or publish the recordings using another program which does not support WMV.
To change the recording format, click Tools >> Settings >> Format.
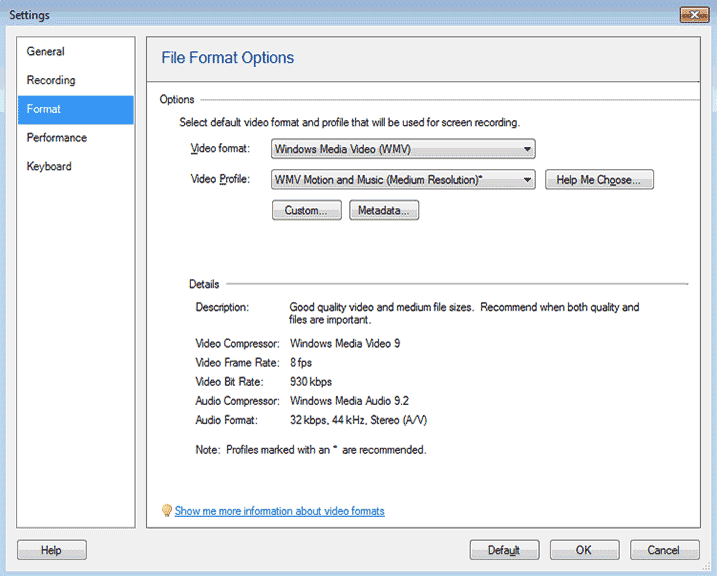
Use the Video Format dropdown list to pick either WMV or AVI.
For both formats, you can pick a Video Profile. Each profile balances file size against video and audio quality. The default is large size and good quality. Recordings made with this Profile are usually indistinguishable from the original screen. If file size is critical you can lower the quality, and if you need extremely high quality with very high image sizes and screen resolutions, you can increase it. Note that a lower-quality profile is likely to work well if you are recording only a small region, because there is less information to save.
Note that using very high quality profiles may cause problems on slower PCs, because recording high quality video and audio can increase the load on the computer's CPU and RAM.
If you are not certain which profile to use, click Choose Profile. The Help Me Choose a Windows Media Profile dialog will appear:
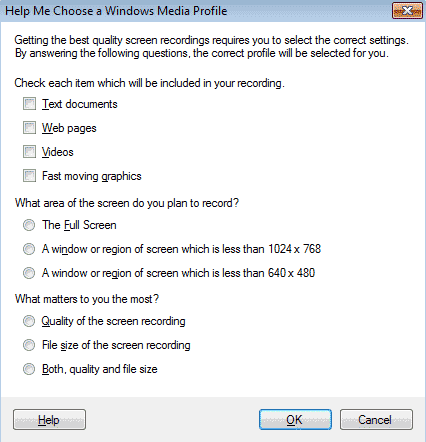
Select the contents of your recording, the area to be recorded, and what aspect of the recording is important to you, then OK. My Screen Recorder will select the best Profile for your purposes automatically.
You can add Metadata to WMV files. Metadata is additional information about the recording that is visible in the player when the file is played back. To add metadata, click the Metadata button. My Screen Recorder supports the following metadata items:
- Title: Select a title for the recording. For example, "Digital Media Converter Pro Tutorial".
- Author: The name of the person recording the video.
- Copyright: The copyright owner, usually a company or the person recording.
- Tags: Video tags are useful when someone is searching for a video file. For instance, if you tag recordings used on your web site with "website", you can use Windows Search to quickly locate them all.
- Description: A brief overview of the purpose or content of the recording.
You can use one, some, or all the metadata options. You do not need to fill in all the blanks.
If none of the supplied profiles suit your needs, click Custom. For both AVI and WMV formats, you can create one Custom Profile, which has the characteristics you choose.
WMV Custom Profile
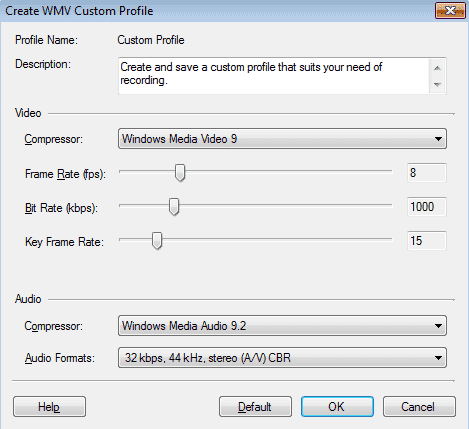
WMV Profiles have the following options:
- Description: It is helpful to use this area to explain what the purpose of the custom profile is, so that you will know when to use it later.
- Video Compressor: Use Windows Media Video 9 Screen in most cases. Windows Media Video 9 is suitable for recording full-motion video, such as using My Screen Recorder Pro to record video playing in a video player. The Windows Media 9 Advanced Profile compressor produces smaller files than Windows Media Video 9, but may not play back well on older PCs or in older versions of Windows. Use Windows Media Video V8 only if the video must play on older PCs or other devices that do not support the newer compressors.
- Frame Rate: The frame rate is the number of times per second the video image updates. Low frame rates can make fast on-screen motion seem "jumpy" or "jerky". High frame rates can make the video look blurry if the Bit Rate (see below) is too low. For most screen capture applications, rates between 5 and 10 are high enough. If you are recording fast motion or capturing video playback, it may improve quality to raise this value.
- Bit Rate: The bit rate is the amount of data used per second to store the video infomation. This is directly related to file size—the higher the bit rate, the bigger the file. It is also very important in determining the playback quality. Generally, higher frame rates and larger image size (either a large region, or high screen resolution) require a higher bit rate to have good video quality.
- Key Frame Rate: Higher key frame rates can make files easier to edit and to seek in, but may require a higher bit rate to produce good quality video.
- Audio Compressor: Windows Media Audio Voice 9 will produce significantly smaller files, but it is not a good choice for compressing any type of audio except the human voice. For the best possible quality, and especially if recording music, select Windows Media Audio 9.2.
- Audio Options: The options are listed from lowest to highest quality. Generally, when using the Voice compressor, the recorded voice will be understandable at settings as low as 5 kbps and can sound good at 12 kbps. Recording using the Windows Media Audio 9.2 compressor you should always use at least 24 kbps, and to record music should probably use at least 48 kbps. You can experiment to determine the lowest value that produces acceptable quality. As mentioned for Bit Rate above, the value selected here directly affects file size.
AVI Custom Profiles
As mentioned at the beginning of this section, AVI files will be larger than WMV files for the same audio and video quality. Use AVI only if you will need to edit or play the recordings with software or a device that does not support WMV files.
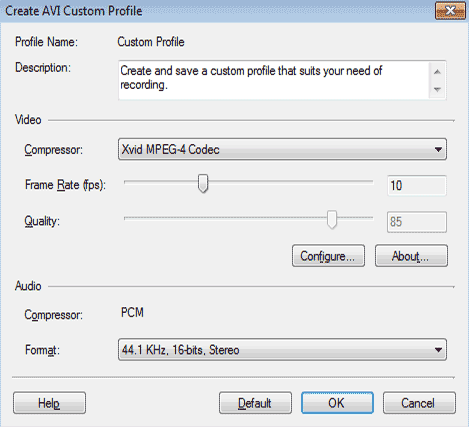
AVI Profiles have the following options:
- Description: It is helpful to use this area to explain what the purpose of the custom profile is, so that you will know when to use it later.
- Video Compressor: The compressors listed here will vary depending on which you have installed on your computer. Xvid MPEG-4 Codec will always be available. Xvid gives very small file sizes with excellent quality and we recommend using it unless you have a specific reason to use a different compressor.
- Frame Rate: The frame rate is the number of times per second the video image updates. Low frame rates can make fast on-screen motion seem "jumpy" or "jerky". High frame rates can make the video look blurry if the Bit Rate (see below) is too low. For most screen capture applications, rates between 5 and 10 are high enough. If you are recording fast motion or capturing video playback, it may improve quality to raise this value. In an AVI file, increasing Frame Rate will also increase the file size. This is not the case when recording in WMV format.
- Quality: The Quality controls how sharp and clear the video image is. It also affects the file size—higher quality produces larger files. Note that this value cannot be adjusted when recording using the Xvid compressor.
- Configure: Press the Configure button to control highly technical details of how video is compressed. The exact settings you can change will depend on the Compressor you select. Unless you are an expert, you can ignore this option.
- Audio Compressor: All AVI recordings made with My Screen Recorder use the PCM compressor, which gives excellent quality.
- Audio Options: The lowest setting in My Screen Recorder is adequate for voice recording, equivalent to telephone calls. The highest settings, using 44.1 or 48 KHz, are equivalent to CD audio. You can experiment to determine which setting is best for your recordings.
To learn more about file formats, read DeskShare's free eBook, the Guide to Computer Audio and Video for Non Experts.
|