|
SSL Protocol and Certificate
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. The SSL protocol was developed by Netscape to enable applications to communicate across a network in a private and secure fashion, discouraging eavesdropping, tampering, and forgery. The SSL works on two protocols. The Record protocol controls the flow of data between the client and server of an SSL session. The Handshake protocol is used to authenticate as well as encrypt and decrypt the data for the session.
SSL Certificate
SSL Certificates are used for encrypting data exchanges between the client and server. Without certificates you can not use SSL connections. A digital certificate, issued by a Certificate Authority (CA), can be assigned to one or both endpoints using SSL. The digital certificate contains a public key and some identifying information that a trusted Certificate Authority has signed.
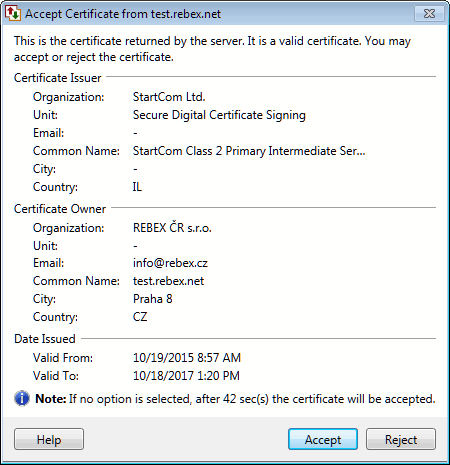
An SSL Certificate will contain information on the Certificate issuer, its owner and the validity dates of the certificate. SSL certificates can be used for the following purposes:
- Authentication: Identify either the client or server.
- Privacy: This ensures that the information is available to the intended users.
- Encryption: Sensitive data like Email messages, files being transferred can be encrypted using a key, so that unauthorized readers are unable to read the message.
- Digital signatures: This provides a strong evidence that the data has not been altered since it was signed and it confirms the identity of the person.
How SSL handshake works
- Step 1:Client connects to a server, secured with SSL. Client requests the server to identify itself.
- Step 2: Server sends a copy of its SSL Certificate, including the server's public key.
- Step 3: Client checks the certificate root against a list of trusted CA's and that the certificate is unexpired, unrevoked, and that its common name is valid for the server that it is connecting to. If the Client trusts the certificate, it creates, encrypts, and sends back a symmetric session key using the server's public key.
- Step 4: Server decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key and sends back an acknowledgement with the session key to start the encrypted session.
- Step 5: Server and Client now encrypt all transmitted data with the session key.
What is an Invalid SSL Certificate
Some of the reasons in which invalid SSL certificate is shown are:
- When the certificate details are incomplete due to server misconfiguration.
- When application is unable to verify the identity of the server.
- When application sense that you are getting connected to a different server which is pretending to be a server you specified, possibly to obtain your confidential information.
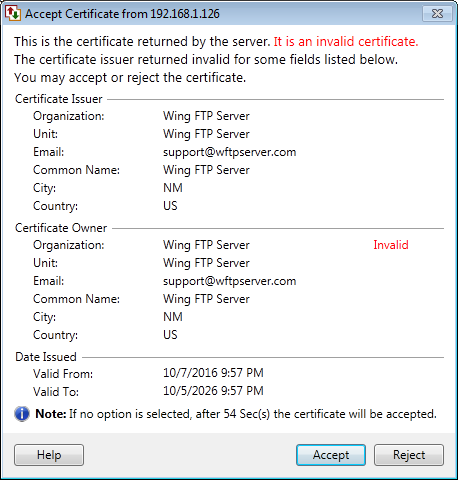
If any exception is received from the server side for issuer, owner or dates, then Auto FTP Manager will show Invalid against the first field of the respective section in the certificate as shown above. For some unknown exceptions, Auto FTP Manager will show the Invalid Certificate but without any Invalid label.
|