|
Export: Save for PC Playback
Select this option to make a movie file designed to be played on a computer directly, not streamed over the Internet or another network.
There are six file types that you can create with Save for PC Playback:
- Windows Media Video (WMV)
- WMV High Definition (WMV HD)
- MPEG Formats (VCD, SVCD, DVD, MPEG 1, MPEG 4)
- QuickTime (MOV)
- Audio Video Interleaved (AVI)
- Digital Video (DV AVI)
Which file format to select depends upon your needs. In many cases, your selection will be determined by what your audience can easily view.
Windows Media Video (WMV) produces very small files of good quality. Viewers on non-Windows computers may need to install a special player to view WMV movies. WMV HD files are very high-resolution WMV files.
QuickTime also produces very high quality, small files. Viewers who are using Windows will need to install the QuickTime Player in order to see movies in that format.
AVI files tend to be larger than either of these formats, but they are ideal if you plan to edit the file again later. DV AVI is a specialized file format used in certain digital cameras and editing equipment. DV AVI files are very large, but also very high quality and editable.
The MPEG formats include two categories: those used if you plan to turn your movie into a disc of some kind (DVD or VCD), and MP4 (MPEG 4) files which offer very high compression (small file sizes) with high audio and video quality. MP4 files cannot be played using the Windows Media Player.
Whatever file format you select, the export procedure is the same.
- Select a file format.
- For that file format, select a Profile. A profile is a complete description of a video file's characteristics. When you select a profile, its properties will be displayed beneath the Select Profile drop-down list in the Profile Details section.
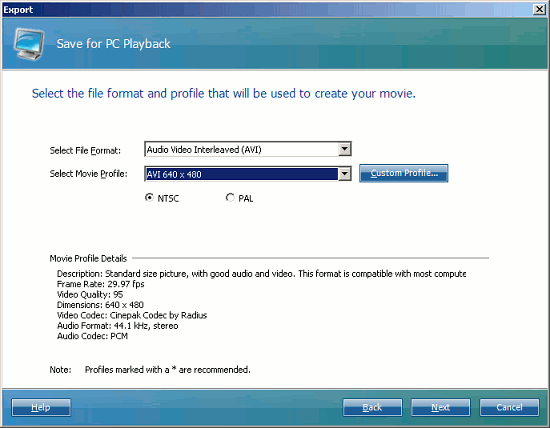
The exact properties shown will vary depending on the file format selected. For instance, DV AVI is not a flexible format and only Frame Rate and Dimensions are shown in Profile Details.
For AVI format only, you can choose to use a Custom Profile, which permits experts to adjust every characteristic of the movie.
- When you have selected a file format and profile, click Next.
- Select a file name and location for your movie:
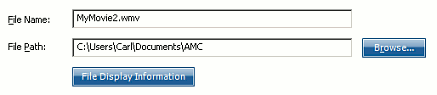
You can either type the complete File Path or press the Browse button and select it. When you have set your file name and path, click Export to create your movie. Depending on the length of the movie, it can take from seconds to hours to complete the export process.
- If you are creating a Windows Media Video (WMV) file, you can create File Display Information. This "metadata" includes a title, genre and other information, and can be displayed during the playing of the movie and also used when searching for movies.
- During the export process, Auto Movie Creator displays certain information: the name of the Output File, its predicted size, the start time of the export, and how long it has been running.
- When the export process is finished, you can click Finish to close the Export window. If you check Preview created movie when finished, the new movie will be played in your default movie player when you click Finish. To open the Windows Explorer showing the folder you exported the movie into, click Open Destination Folder before clicking Finish.
Which format should I select?
When saving a file for playback on a PC, you have several possible file formats to use, each of which can produce good results. Here are our recommendations:
- If you will be editing the movie again, use AVI or DV AVI. DV AVI produces very large files, but has extremely high quality. AVI files are easy to edit and if you pick a high-quality profile, will produce excellent results.
- If storage space is a major concern, use MP4, WMV, or QuickTime. MP4 is the newest format, and some PCs may have trouble playing these files, but they give excellent file compression (small size) with good quality. WMV (Windows Media Video) and QuickTime (MOV) also give excellent compression and quality. Generally, Windows users will have to install special software (such as the QuickTime Player ) to play MP4 or MOV files, while Apple Macintosh users will have to install special software to play WMV files.
- If compatibility with the widest possible number of computers is a concern, use MPEG 1 or MPEG 2 video. These standards are quite old, and their compression is not as good as the newer formats, but almost any video software can play back MPEG 1 and 2 files.
- If your video is high definition—for instance, a recording of HDTV signals—and you will be using WMV as your file format, use WMV (High Definition). The picture quality of these files is exceptionally good. High definition profiles for MP4 and QuickTime are included in the main list of profiles for those formats.
|